Understanding Frostbite and Hypothermia: Risks, Symptoms, and Prevention
Posted On:
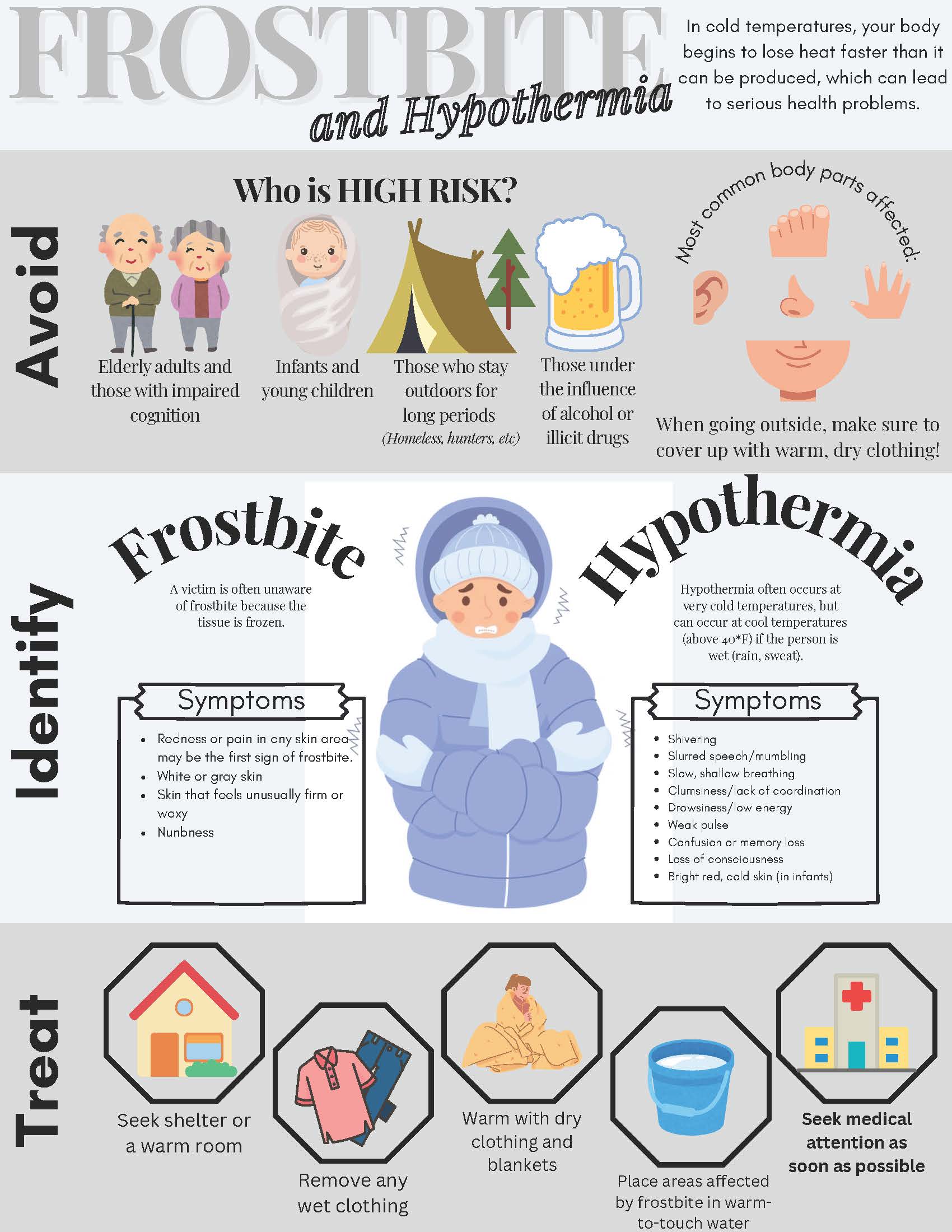
Understanding Frostbite and Hypothermia: Risks, Symptoms, and Prevention
Frostbite and hypothermia are serious cold-weather conditions that can have severe consequences if not properly addressed. Here's an overview to help you stay safe during chilly conditions.
Who Is at Risk?
Certain groups are more vulnerable to frostbite and hypothermia, including:
- Elderly adults and individuals with impaired cognition.
- Infants and young children, whose body temperature regulation is less effective.
- Those under the influence of alcohol or drugs, which can impair judgment and response to cold.
- People who spend extended time outdoors, such as the homeless, hunters, or outdoor workers.
Commonly Affected Areas
Frostbite typically impacts exposed body parts like fingers, toes, ears, and the nose.
Recognizing Symptoms
- Frostbite:
- Redness or pain in exposed skin areas.
- White or grayish skin with a firm or waxy texture.
- Numbness.
- Hypothermia:
- Shivering, slurred speech, and shallow breathing.
- Clumsiness, confusion, or memory loss.
- Drowsiness, a weak pulse, or bright red skin in infants.
Prevention Tips
- Wear warm, dry clothing that covers all exposed skin when venturing outside in cold weather.
- Stay dry, as wet clothing accelerates heat loss.
Treatment Steps
- Move the affected person to a warm shelter or indoors.
- Remove any wet clothing and replace it with dry, warm layers.
- For frostbite, submerge affected areas in warm (not hot) water.
- Seek medical attention immediately for severe symptoms.
By understanding and recognizing the risks and symptoms of frostbite and hypothermia, you can take proactive measures to prevent and treat these conditions effectively. Stay prepared and stay warm!